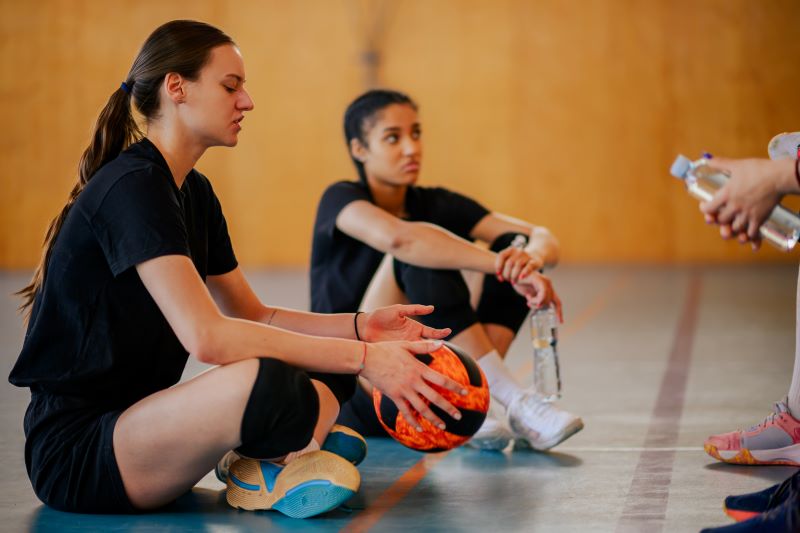
Sports are known to improve physical health, but what about mental health? Mental health is a significant part of overall health and well-being. Mental health and sports go hand in hand. Sports help lower stress, improve energy, alleviate symptoms of depression and anxiety, and improve cognitive ability. Wintrust Sports Complex is the perfect spot for kids and adults to engage in sports and improve their mental health.
What is Mental Health?
The term “mental health” seems to be everywhere. The exact definition depends on context and usage, but generally, mental health includes psychological and social well-being, as well as emotional health and regulation.
Aspects of mental health include self-acceptance and confidence, maintaining healthy relationships, cognitive ability, and habits and behavior. Mental health impacts nearly every aspect of someone’s life. Social life and relationships, education, work, physical health, and overall quality of life.
Some factors that impact mental health are harder to control. Genetics, brain chemistry, trauma, environmental and living conditions, access to care, and culture all impact mental health. Globally, events like the COVID-19 pandemic, natural disasters, and mass tragedies can negatively affect mental health, even for individuals indirectly impacted.
Maintaining and improving mental health is a key part of a well-balanced, well-rounded lifestyle. The combination of implementing coping strategies, a support system, and lifestyle changes have positive, lasting impacts on mental health.
Lifestyle changes such as adjusting sleep habits, maintaining a healthy and balanced diet, exercising regularly, and participating in sports help mental health.

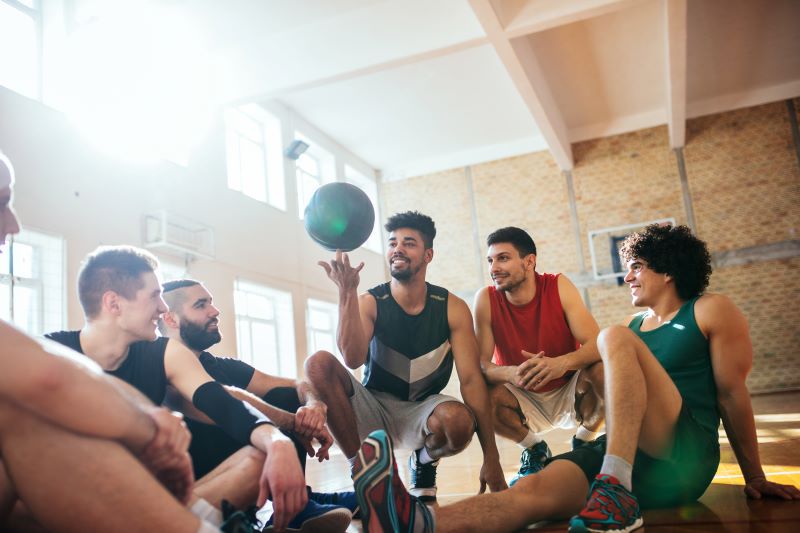
The Mental Health Hormones
Positive mental health is related to the “happiness hormones,” or the set of chemicals in the brain that play a significant role in regulating mood, emotions, and overall well-being.
Serotonin
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that helps regulate mood, anxiety, and happiness. It also influences sleep, appetite, and digestion. Low serotonin levels are associated with depression and anxiety.
Dopamine
Known as the “feel-good” hormone, dopamine is associated with pleasure, reward, and motivation. Dopamine is a feeling you get when you cross a task off a to-do list or receive a reward. It’s the brain’s way of reinforcing positive behaviors.
Endorphins
Endorphins are the cause behind a “runner’s high.” They are natural painkillers released in response to stress, pain, or discomfort. They help alleviate pain and induce feelings of euphoria and well-being.
All three of these happiness hormones have one major thing in common. All of them are increased by physical activity and exercise. Positive social interactions, engaging in hobbies, and achieving goals also release these hormones. One activity that combines exercise, social interactions, hobbies, and feelings of accomplishment is sports. This is just one of the benefits of sports to mental health.
How Sports Help Mental Health
On a basic level, sports help mental health by releasing happiness hormones. On a deeper level, the impacts of mental health and sports include stress reduction, improved self-esteem and confidence, better focus and concentration, social benefits, building resilience and perseverance, improved sleep, and developing lifelong health habits for the body and mind.

Stress Relief
One of the most common impacts of mental health and sports is a decrease in stress levels. Stress can extend beyond mental health and lead to physical symptoms, including headaches, upset stomach, elevated blood pressure, chest pain, and problems sleeping. At least 60% of primary care doctor visits in the USA involve some stress-related component or complaint. Engaging in sports and any form of exercise for just 30 minutes a day can have immediate impacts on stress levels.
Addiction
Mental health and sports even relate to addiction and positive decision-making. Youth athletes have a lower chance of smoking, drug use, and engaging in risky behavior. Dopamine is often related to addiction through pleasure. Achieving that same feeling from exercise rather than substances is a key way sports help mental health.
Productivity and Cognitive Ability
Sports and mental health both impact cognitive ability and brain function. Any level of physical activity is associated with improved academic achievement, enhanced concentration, and attention in the classroom. High school athletes are more likely than non-athletes to attend college and earn a degree. The impacts of sports continue through adulthood. Adults who were physically active as children are more productive at work, and a large percentage of female corporate executives played a sport.
Anxiety and Depression
Anxiety and depression are two of the most common mental health diagnoses. One study shows that exercise can be as effective as standard antidepressant treatment. While sports may not replace other interventions, especially for severe cases of anxiety and depression, they can help. Studies also show that children who reported no exercise were twice as likely to have mental health problems, especially related to anxiety and depression, compared to those who regularly exercise.
Team Sports and Mental Health
The benefits of sports to mental health increase during team sports compared to individual sports and exercise. Team sports provide social interaction, support, and community. Sports often provide safe environments to learn new skills, build friendships, and engage in healthy competition.
Team sports and competition also help develop emotional maturity and regulation. Participation in sports teaches individuals how to handle losses and failures constructively and overcome setbacks. Athletes also gain skills in problem-solving, handling stress, and resilience.

Balancing Sports and Health
While sports have many benefits, sometimes those benefits can cross a line into negative impacts. Too much stress and pressure from coaches, teammates, parents, or internally can lead to burnout and anxiety. Depression can impact athletes, especially when their sport is their main coping mechanism. Injury or the off-season can increase the risk of depression in athletes. Eating disorders, including orthorexia, the eating disorder characterized by an excessive preoccupation with eating healthy food, are increasingly common among athletes.
Ensuring athletes at all levels, as well as parents and coaches, have the proper education and awareness about the potential harmful mental health impacts of sports greatly lowers the risk. Building a sports environment that allows participants to be honest open, and take breaks as needed in order to maintain positive mental health is critical.
Wintrust Sports Complex
Wintrust Sports Complex understands the mental health benefits of sports. Our facility is the regular practice and home gym for multiple different local youth sports teams. Our summer camps and programs provide a safe, supportive space for kids to learn new skills and improve their mental health. Even our arcade and laser tag provide ways to relieve stress. Bring the whole family to engage in the benefits of sports!